Market Basics
How reliable are the trading indicators?
Are trading indicators the secret to successful trading? Can they truly guide you to profitable trades? These questions have intrigued traders and investors alike for years. Trading indicators, the mathematical computations based on historical volume and price data, are designed to provide insights into price changes, trends, and potential buying or selling opportunities.
Hello readers, hope the markets are blessing you with profits. In this article, we will find the answer to the long-debated topic. Let’s dive into the world of trading indicators and uncover their potential impact on your trading journey. So, buckle up!
What are Trading Indicators?
Trading indicators are mathematical computations based on historical volume, price data, or both. These indicators are frequently employed to assess price changes, spot trends, and produce buy or sell signals. They are designed to give traders unbiased assessments of the state of the market and probable price changes in the future.
In the realm of financial markets, trading indicators are important because they give traders information and indications so they can make wise judgments. Moving averages, the relative strength index (RSI), the stochastic oscillator, and Bollinger Bands are a few examples of popular trading indicators. Although all indicators have the same work of notifying the trader. They differ from each other in one way or another. Each indicator uses a unique set of algorithms and criteria to produce signals.
Pros of Trading Indicators
-
Neutral analysis–
Trading indicators give investors unbiased information and viewpoints, reducing emotion from trading judgments. They assist traders in making decisions based on statistical analysis as opposed to just intuition or personal judgment.
Regulating emotions is a must for every trader. Emotions like pride, greed, fear or not accepting fault can lead to significant losses.
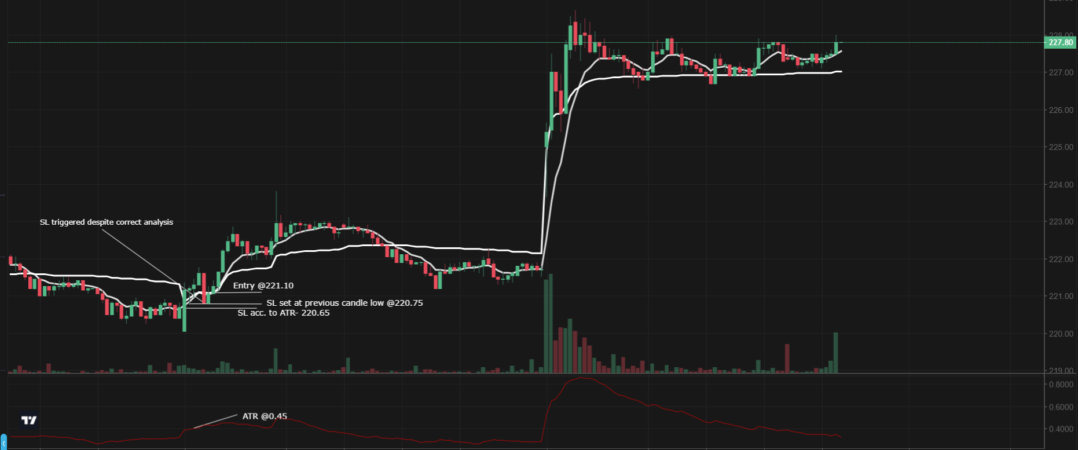
For instance, let’s consider a hypothetical scenario where a trader identifies a head and shoulders formation and believes it’s a signal to go short. However, despite this analysis, the price continues to hold above the simple moving average (SMA) with significant trading volume. Despite receiving indications that go against his initial analysis, the trader disregards the signals and proceeds with the short position. Unfortunately, the price unexpectedly breaks the resistance level and continues to rise, resulting in the activation of the stop-loss order.
Thus, trading indicators reduce such human errors by giving unbiased information. -
Price action confirmation–
Indicators can be used to verify or validate price action. Trading decisions can be more dependable when price analysis and indicator signals are combined since it gives traders a more complete understanding of the market dynamics.
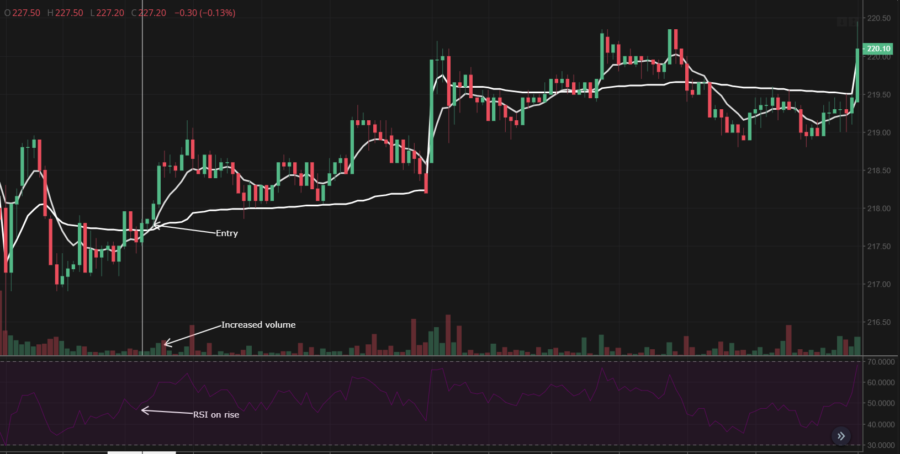
For example, suppose a trader identifies a double bottom pattern accompanied by a significant increase in trading volume, which suggests a potential bullish trend. With this observation, the trader decides to go long and enter a buying position. To further validate this analysis, the trader turns to the Relative Strength Indicator (RSI). if the RSI starts moving beyond the oversold zone or shows a steady increase in value, it typically signals a buying opportunity. The trader’s decision to go long is further supported by this confirmation from the RSI.
-
Risk Management–
By revealing market volatility and probable reversals, trading indicators can help manage risk. Based on indicator readings, traders can set stop-loss levels, trailing stops, or take-profit objectives to help safeguard capital and reduce losses.
The Average True Range (ATR) serves as a useful indicator for determining stop-loss levels. For instance, with an ATR value of 0.45, if a trader takes a buy position at 221.10 and sets the stop loss at 220.65. If based on ATR, it could have withstood sudden volatility and resulted in profits. However, in this example, the stop loss was triggered within 10 minutes, despite the price continuing to reach new highs afterward. -
Entry and Exit information–
Indicators generate information and their interpretation can help traders decide on entry and exit points. Using this information, traders can strategically plan their positions to maximize profits and reduce losses.
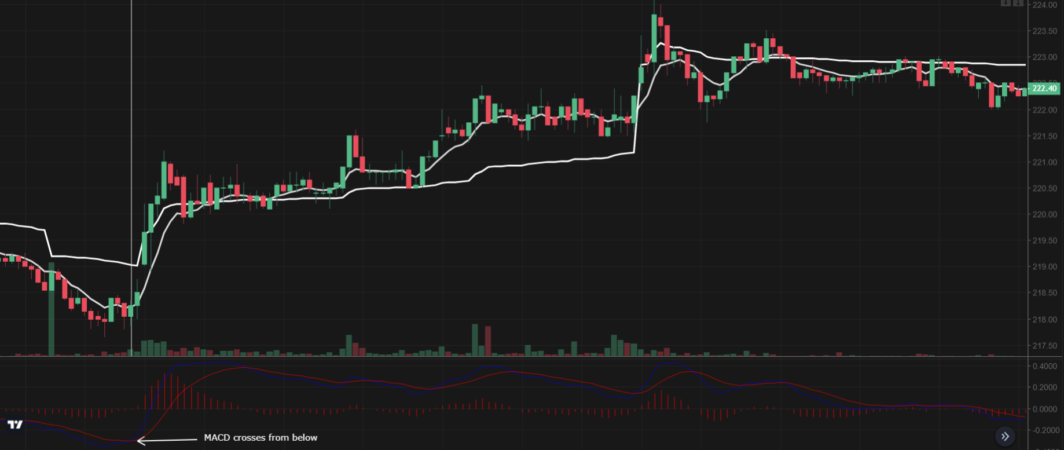
For example, the MACD indicator is a valuable tool for traders in determining to buy or sell opportunities. When the MACD line crosses above the signal line, it signals a buying opportunity. By considering price action and confirming the strength of the move, traders can enter a long position and potentially profit.
Cons of Trading Indicators
-
False Signals-
Trading indicators are not perfect and sometimes give you erroneous or misleading information. These wrong signals may result in poor trading choices and possible losses.
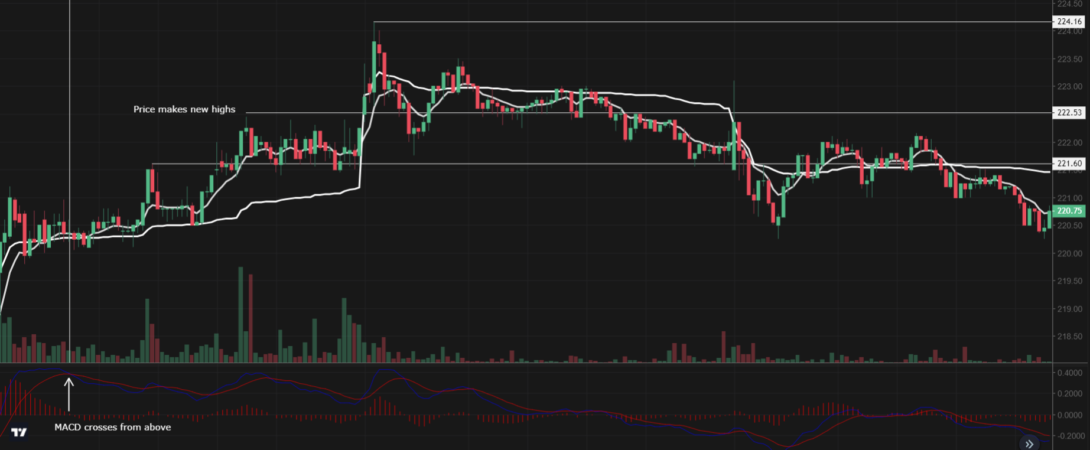
For example, an indicator might give a buy signal even though the market is moving sideways.
To verify the accuracy of indicator signals, traders must use caution and further research.
-
Lagging indication–
Most indicators are lagging in nature. That means by the time a signal is generated, the price may have already moved. Trading indicators lag behind real-time market moves since they are based on historical price data. Therefore, traders must keep price action in check and keep looking for potential movements.
-
Complexity –
In the present scenario, there is a vast array of indicators available. This makes it easier to get confused over what to use and can lead to wrong analysis. Such mistakes can often lead to big unrecoverable losses, especially for new traders.
Take a look at this image. See how complex and difficult it gets to make an analysis due to too many indicators.
-
Over-Reliance–
New traders often rely too heavily on indicators, treating them as shortcuts for easy profits. They neglect personal analysis and blindly follow indicator signals, leading to unsustainable trading. Consequently, they lose their capital quickly and leave the market prematurely, never truly beginning their trading careers.
To avoid this pitfall, traders must not only rely on indicators but also prioritize enhancing their analysis and judgment skills. Ultimately, it is a sound analysis that will drive their trading career and yield profitable outcomes.
Do Trading Indicators even work?
So, again it all boils down to the same question. Do trading indicators even work in real-time trading? The short answer is Yes*, they do.
* Is for terms and conditions applied. Not some complex insurance terms, just simple practical information.
- One important detail to keep in mind about trading indicators is that what they provide should be taken as information. This ‘information’ should then be interpreted and not blindly followed as a sign from the heavens to initiate a trade.
The work of an indicator is to make a trader’s job easy and act as a confirmed, not the decision maker. In the end, it is the market analysis that will lead to sustainable profits and wealth creation. - The use of indicators comes with strictly managing the trading style. Decide in advance what indicators on what settings you will use for different time frames. Also, keep a limit to the number of indicators being used, since it can cause information overload and lead to bad trades.
- If you are new to trading, focus more on building your analysis rather than finding indicator-based strategies. There is an ocean of strategies available online, promising up to 90 percent accuracy. They could, but ask yourself, can you deliver the same results as a newbie with your limited skills? Can you make quick decisions and changes to the strategy as per the market shifts?
Because reality is cruel, markets are dynamic and unpredictable. Following such a standard approach in an ever-changing scenario is next to impossible. At least in the long run.
In conclusion, trading indicators do work, but they should be used as tools for information and confirmation rather than as decision-making mechanisms. Proper risk management, limiting the number of indicators used, and focusing on building analytical skills are key aspects of successful trading. Ultimately, it is the trader’s ability to adapt and analyze the ever-changing market conditions that will lead to long-term profitability and success.
Finance World
Understanding Contingent Liabilities: Implications and Risks for Companies

Introduction
Due to the potential to significantly impact a company’s financial situation and outlook for the future, contingent liabilities are crucial in financial reporting. These liabilities are potential debts that could be owed due to past incidents but they are unsure whether they will come to pass due to upcoming circumstances. Because of their inherent uncertainty, companies must carefully evaluate how to recognize, assess, and disclose these commitments in their financial statements.
Understanding Contingent Liabilities
As prospective obligations depend on unforeseen future occurrences, contingent liabilities are crucial to financial reporting. The company defers the recording of these liabilities on the balance sheet as actual obligations until the occurrence of the triggering event is likely or inevitable.
Recognition and Measurement
To account for contingent liabilities, businesses follow accounting guidelines like Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) or International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS). Two important requirements must be met for contingent liabilities to be recognized:
- Probability
The business assesses the chance that the unknown event will materialise. If the contingent obligation is probable, or more likely than not, it is recorded in the financial statements and properly stated.
- Measurability
This second criterion examines whether it is possible to calculate the contingent liability’s amount with accuracy. The corporation assesses the liability and makes a provision on the balance sheet to reflect its prospective effect on its financial situation if it can make a reasonable assessment.
Managing Contingent Liabilities
Companies must manage and reduce contingent liabilities in order to maintain their financial health and secure shareholder interests. The following are important tactics that businesses can use to proactively handle contingent liabilities:
- Risk Assessment
Regular and thorough risk assessments are essential for identifying potential risks and exposures that could result in these liabilities. Companies can create suitable risk mitigation plans by analysing various risks’ likelihood and potential impact.
- Insurance
Enough insurance protection is crucial for guarding against possible losses brought on by prospective liabilities. Companies should conduct a thorough risk assessment and invest in insurance plans that address the necessary risks.
A few examples of this kind of insurance are general liability, product liability, directors and officers (D&O) liability, and professional liability. Insurance acts as a safety net, minimizing the negative effects of these liabilities on the company’s financial statements and protecting cash flow.
- Contractual Protections
Limiting potential liabilities requires carefully structured contracts. The obligations, responsibilities, and extent of each party’s liabilities in the event of a disagreement can be specified through clear and explicit contract terms. Including dispute resolution techniques like arbitration or mediation can aid in problem-solving more quickly and affordably.
Impact on Investors and Stakeholders
Contingent liabilities can greatly impact how stakeholders and investors see a company’s management, stability, and financial health. There are numerous approaches to observing the impact on investors and stakeholders:
- Valuation
Potential contingent liabilities may directly impact a company’s valuation. When calculating the company’s value, analysts and investors consider the inherent risks. If the firm’s these liabilities are substantial and their potential impact is severe, investors may give the company a lower valuation, which would cause the stock price to decline.
- Creditworthiness
When determining a company’s creditworthiness, lenders and creditors pay special attention to its contingent liabilities. High contingent liabilities could make it difficult for the business to fulfill its financial commitments, including debt repayments.
- Shareholder Confidence
Establishing and sustaining shareholder confidence requires open disclosure of contingent liabilities. When businesses provide clear and thorough information, investors and stakeholders are better informed about the company’s exposure to uncertainty. This can be achieved by describing potential risks and how they will be managed in the financial statements’ footnotes.
This openness encourages confidence in the company’s management and its dedication to overcoming possible obstacles.
Conclusion
The effective management of contingent liabilities is essential for a company’s long-term survival in today’s fiercely competitive business world.
Companies can ensure financial stability and sustainability by proactively managing these liabilities. This allows them to focus on innovation, growth, and strengthening their market position, thereby generating value for all parties involved.
Follow us at TradeAlone.com to stay updated with the latest market news.
Market Basics
The Impact of Options Trading on Stock Prices: A Comprehensive Analysis

Options trading can have a significant impact on stock prices, both directly and indirectly. In this article, we will explore the various ways in which options trading influences stock prices, including through delta hedging, volatility effects, and market sentiment.
1. Delta Hedging
Delta hedging is a trading strategy used by investors to mitigate the risk of changes in the price of an option by buying or selling the underlying asset. For instance, if an investor purchases a call option on a stock, they may also buy shares of the stock to offset the risk of a potential price decrease. This buying pressure created by delta hedging can contribute to pushing up the stock price.
2. Volatility Effects
Volatility plays a crucial role in options trading and can indirectly impact stock prices. Options prices tend to be higher when there is higher market volatility and lower when volatility is low. Investors are willing to pay more for options when they expect significant price movements in the underlying asset. Thus, an increase in options trading activity can lead to higher volatility in the underlying asset, which, in turn, may result in higher stock prices.
3. Market Sentiment
Options trading can be a reflection of market sentiment, which is a measure of how bullish or bearish investors feel about a particular asset. When there is a substantial amount of options trading on a specific stock, it can indicate a strong bullish or bearish sentiment towards that stock. This sentiment can influence stock prices in the direction of the prevailing sentiment.
4 . Supply and Demand Dynamics

The primary ways options trading impacts stock prices is through changes in supply and demand dynamics. As investors buy and sell options contracts, it affects the perceived interest in the underlying stock. When there is a surge in demand for call options (the right to buy the stock), it indicates bullish sentiment, potentially leading to higher stock prices. Conversely, an increase in demand for put options (the right to sell the stock) signals bearish sentiment and could result in lower stock prices.
5. Volatility and Implied Volatility
Options trading can introduce additional volatility to the stock market. The prices of options themselves are influenced by market volatility expectations, which are measured by implied volatility. If there is heightened uncertainty or news events surrounding a stock, implied volatility may rise, leading to more expensive options. As a result, the stock price may experience larger swings as traders adjust their positions to factor in the changing volatility.
6. Options Expiration and Pinning
Options have an expiration date, and as that date approaches, traders may adjust their positions or decide to exercise their options. This behavior can lead to increased trading activity and volatility as the expiration date nears. Additionally, “options pinning” or “options max pain” refers to the phenomenon where the stock price gravitates toward the price that causes the most options contracts to expire worthless, benefiting options writers. This pinning effect can influence short-term stock price movements, especially around expiration dates.
7. Hedging Strategies
Market makers and professional traders use options as part of their hedging strategies to manage risk in their portfolios. When they sell options, they often hedge their positions by buying or selling the underlying stock. This hedging activity can affect the stock’s price by creating additional buying or selling pressure. For instance, when market makers sell call options, they may buy the underlying stock to hedge against potential losses, leading to increased demand and higher prices.
8. Impact on Investor Sentiment
Options trading can impact investor sentiment and perception of a stock. Unusual options activity, such as a surge in call buying, may be interpreted as a signal of positive expectations for the stock’s future performance. On the other hand, heavy put buying might lead to negative sentiment and dampen the stock’s price.
9. The Small and Indirect Impact
While options trading can have a notable impact on stock prices, it is essential to understand that this influence is typically more pronounced in the short term rather than the long term. The effects can be more significant for highly liquid stocks with higher volatility levels. However, in general, the impact of options trading on stock prices might be small and challenging to predict due to the complexities of the options market and other influencing factors.
Option Pricing Model
Here is a table of the most common option pricing models:
| Model | Description |
|---|---|
| Black-Scholes model | A mathematical model that uses five inputs to price options: the strike price, the current stock price, the time to expiration, the risk-free rate, and the volatility. |
| Binomial model | A discrete-time model that prices options by assuming that the underlying asset can only move up or down by a certain percentage in each time step. |
| Monte Carlo model | A simulation-based model that prices options by randomly generating a large number of possible price paths for the underlying asset. |
| Heston model | A stochastic volatility model that prices options by assuming that the volatility of the underlying asset is itself a stochastic process. |
| SABR model | A simplified version of the Heston model that is easier to calibrate and use. |
The Black-Scholes model is the most widely used option pricing model, but it is not without its limitations. The model assumes that the underlying asset follows a geometric Brownian motion, which is a continuous-time random walk. This assumption is not always accurate, especially in the short term. The Binomial model and the Monte Carlo model are more accurate than the Black-Scholes model, but they are also more computationally expensive.
The choice of which option pricing model to use depends on a number of factors, including the type of option, the time to expiration, and the volatility of the underlying asset. In general, the Black-Scholes model is a good starting point, but it may be necessary to use a more complex model if the underlying asset is volatile or if the option has a long time to expiration.

| Model | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Black-Scholes model | Simple to use, widely available | Assumptions may not be accurate |
| Binomial model | More accurate than the Black-Scholes model | Computationally expensive |
| Monte Carlo model | Most accurate option pricing model | Computationally very expensive |
| Heston model | More accurate than the Black-Scholes model | Assumptions may not be accurate |
| SABR model | Simplified version of the Heston model | Less accurate than the Heston model |
Conclusion
Options trading can exert both direct and indirect influence on stock prices. Delta hedging can create buying pressure on the underlying asset, pushing up stock prices. Volatility effects can result in increased options prices and subsequently higher stock price fluctuations. Additionally, options trading activity can reflect market sentiment, leading to stock price movements in the direction of prevailing sentiment. However, it is important to recognize that the impact of options trading on stock prices is typically more pronounced in the short term, and predicting its effects can be challenging. As with any investment activity, thorough research and consideration of the risks are crucial when engaging in options trading.
Visit Tradealone for more Updates
editor
What is Earnings per share (EPS) of a company?

What is the EPS of a company?
A simple and unbending meaning of EPS is Earnings per Share of the company. What is known as the earnings of a company? The earnings of a company refer to its net income, which is obtained after deducting the cost of goods sold (COGS), operating expenses, interest, and taxes from its total sales revenue. If we take a P&L statement of a company, the total revenue of a company is seen in the initial line items. This is followed by COGS, operating & admin expenses, and then interest and tax expenses. A P&L statement gives an investor the outline of the company’s earnings.
The formula to calculate the EPS of a company is EPS=Net income of the company/Total number of outstanding shares.
EPS is profit that belongs to the shareholders and it says us how much profit a company has earned for every share issued. Without much more explanation, let us go to the core of the article.
Let us see factors that fuel the EPS growth of a company
Factors Fuelling EPS Growth
- Increase in sales
- Increase in productivity
- Reduction in costs
- Reduction in interest caused by debt
- Expansion of business
Increase in sales
A company always aims to increase sales, but the strategies it uses makes a difference. The most effective way a company can improve its sales is by
- Establishing a better connection with customers by providing user-friendly products
- Use proper marketing and sales strategy to develop the business
- Improving the business model of the company by being financially healthy, engaging risk management, and hiring an efficient management team which propels future growth.
Increase in productivity
A company’s productivity increases when the employees make better use of their opportunities. The ways the company achieves it are
- Providing a learning platform for employees
- Implementing a flexible and attractive work culture.
- Paying the right worth of salary.
- Implementing the latest technology to attain efficiency.
Reduction in costs
The net income of a company can be improved in 2 ways. One happens when revenue is given importance, the other way is cutting costs. After all revenue and expenses form the crux of net income.
A company will handle different ways to cut its costs, they may lay off employees, close additional facilities, streamline supply-chain, cut costs on marketing and sales strategies, reduce outsourcing of work and hire efficient professionals and much more strategies are followed by companies to cut costs.
Reduce debt and interest
Debt is an obligation that involves a debtor and a creditor. Companies often borrow debt to expand their businesses or to fund the current business cycle. We can find debt in the liabilities section of a balance sheet. There as long-term and short-term debt. However, if a company’s current assets are higher enough to clear the debt the companies are debt-free. This debt incurs interest which weighs loads on the profitability of the business. Lesser the debt the company can have high earnings and eventually higher EPS.
Expansion of business
When a company wants to expand it is evident that the company has a well-established business. By expanding the company can acquire new customer concentration, increase profits, and launch new products or services. The most important strategy of expansion is eliminating insecurity held over a single market. Diversification happens and the company no longer needs 1 client or the same set of clients for its profits. This ultimately results in higher profits if the company plans strategically on expansion.
We understood the ways a company can increase its Earnings and ultimately the EPS. Now let us see a few companies which give consistent EPS growth over the years.
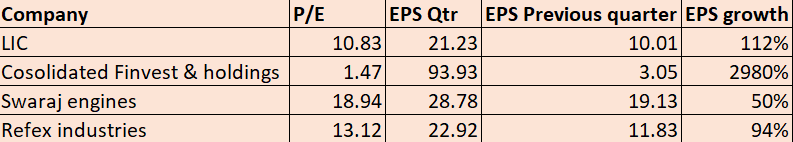
In this table, we can see a few stocks whose EPS grew innumerably higher from quarter to quarter.
We previously saw how an organization can improve its EPS through various steps, but consistency is the key. A company whose EPS growth is consistent over a period is very much attractive to investors.
How can an Investor profit from companies with consistent EPS growth?
- EPS gives is a direct synonym for a company’s profitability. A company that is financially stable gives steady EPS growth over the years.
- One of the crucial valuation ratios the PE ratio and PEG ratio depends on the value of EPS. The higher the EPS, the lower will be the PE ratio and companies with low PE ratio consistently attracts investors owing to their undervaluedness.
- Any investor considers 2 criteria before investing. One is the price appreciation of the asset, another is the periodic return generated. Which is also known as a dividend. A company with consistent growth in earnings indicates confidence in shareholders. An investor will prefer a company with a consistent dividend payout compared to one which is irregular in the payment of dividends.
- The company with consistent earnings growth looks promising and the market anticipates good future potential. This increases the price of the stock from which the investor gains profit.
Incorrect earnings
Sometimes the company registers an incorrect revenue in the P&L statement to create false beliefs about the company. They do this by holding the revenue of earlier quarters and accounting in them in consequent quarters to manipulate the investors despite the huge competition in the market regarding QoQ results. It is appropriate to look for the earnings transcript call in the investor presentation which explains the detailed revenue growth of the company.
In this article, we understood the meaning of EPS and the factors which fuel EPS growth. A table showing companies with excellent EPS QoQ growth was depicted. And we saw why a company with consistent EPS growth seems attractive to investors. EPS is a powerful metric when it is compared with its peers, or industry or even when it is compared over a period of time. EPS in solitary doesn’t depict the true picture of the company. An investor has to analyze the line items in the P&L statement beforehand. If the company registers consistent earnings growth, lies in blue ocean technology, is defensive to cyclicality, reduced debt, and controls expenses, you have spotted a multi-bagger!
-
 Profit Making Idea1 year ago
Profit Making Idea1 year agoThe Grandfather Son (GFS) Strategy: A Technical Analysis Trading Strategy
-

 Uncategorized8 months ago
Uncategorized8 months agoA BJP victory and the Stock Market: what to expect this monday
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoInnovative Metro Ticketing Revolution in Pune by Route Mobile and Billeasy’s RCS Messaging. Stock trades flat
-

 editor9 months ago
editor9 months agoHow to research for Multibagger Stocks
-

 Trending12 months ago
Trending12 months agoDoes the “Tata-Apple venture” benefit Tata shares?
-

 Finance World12 months ago
Finance World12 months agoHow Zomato Turned Profitable: A Landmark Achievement in the Indian Food Delivery Market
-
 Market ABC8 months ago
Market ABC8 months agoSpotting an operator game: How to do it?
-

 Market ABC1 year ago
Market ABC1 year agoThe Pullback Strategy: A Timeless Approach to Investment Success